Professor James Goodwin (PhD), Director of Science and Research Impact, the Brain Health Network, and author of Supercharge Your Brain enlightens us on the most complex organic structure in our known universe. Let’s learn how your brain works.
Packed into the confines of our cranium, our two-pound brain contains some 85 billion neurones (grey matter), 86 billion support cells, up to 200,000 synapses per cell and enough fibers (white matter), to reach the moon and back.
In terms of oxygen consumption, our brain is immensely thirsty with 20-25% of the total for all other metabolic needs, equating to some 500 calories per day. This level of metabolic privilege is due to the fact that the activity of the brain controls not only all aspects of our basic survival mechanisms, such as body temperature, water, pH, blood pressure, hormone regulation, posture, balance, and movement, but all of our higher-level thinking, planning, and decision making, our social engagement and our emotional control.
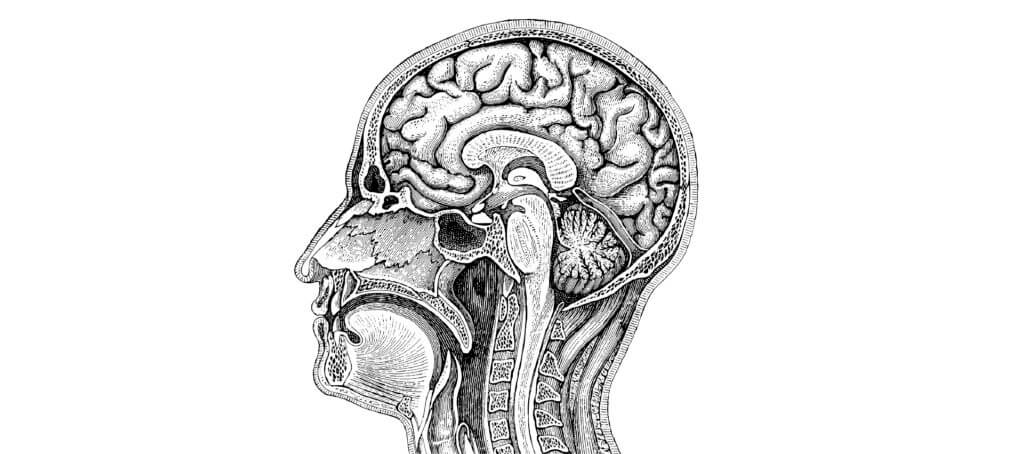
Modern neuroscience has moved away from the idea of ‘localization of function’ (ascribing certain functions to particular parts of the brain). In fact, thousands of distinguishable areas can be identified within the brain, based on fine distinctions of neural structure, chemistry, and connectivity, with many brain functions integrated across disparate areas. However, neuroanatomists traditionally divide the brain into six main regions:
Cerebral hemispheres (telencephalon), Diencephalon (thalamus and hypothalamus), Mesencephalon (midbrain), Cerebellum, Pons, and Medulla Oblongata

1. The Cerebral Hemispheres (Telencephalon)
This co-ordinates the operations of virtually all the brain and are responsible for our conscious thoughts, planning, decision making, and our higher mental functions, such as reasoning
2. The Diencephalon
• The Thalamus is a vast processing and relay centre for incoming sensory data and controls much of our basic ‘consummatory’ behaviors (eating, drinking, sexual activity, and so on)
• The Hypothalamus regulates many of the vital, subconscious, control systems of the body, such as blood pressure, body temperature, and the release of hormones
3. The Mesencephalon (Midbrain)
This is part of the brainstem and is associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation
4. The Cerebellum
A highly sophisticated regulating system for the control of smooth movement and posture
5. The Pons
Controls voluntary often, but simple acts such as sleep, respiration, swallowing, bladder function, equilibrium, eye movement, facial expressions, and posture
6. The Medulla Oblongata
This is situated at the base of the brain and maintains vital centers such as respiration and cardiovascular control
So that’s an overview of how your brain works. Optimizing your brain function with your favorite playlist? Ideal! Here’s HOW MUSIC CAN BOOST OUR BRAIN POWER